Blog

Blog

Blog

How to Understand Glutamic Acid Residue Effects in Proteins?
Understanding the effects of glutamic acid residue in proteins is crucial for biochemical research. Glutamic acid residue plays an essential role in the structure and function of proteins. This amino acid influences protein folding, stability, and interactions. Its charged side chain can form hydrogen bonds and salt bridges, making it pivotal in enzyme catalysis and substrate binding.
Despite its importance, the exact mechanisms remain partially unclear. Different proteins react uniquely to glutamic acid residue changes. These variations can lead to unexpected outcomes in protein function. Experimentation often yields mixed results, highlighting a need for deeper investigation. Issues can arise when researchers overlook subtle effects of this residue.
Reevaluating the role of glutamic acid residue may reveal new insights. Understanding its impact on protein dynamics could lead to innovative drug designs. The complexity of protein interactions means that every detail matters. Researchers must remain open-minded and critical about their findings. This approach will help unravel the intricate role of glutamic acid residue in biological systems.
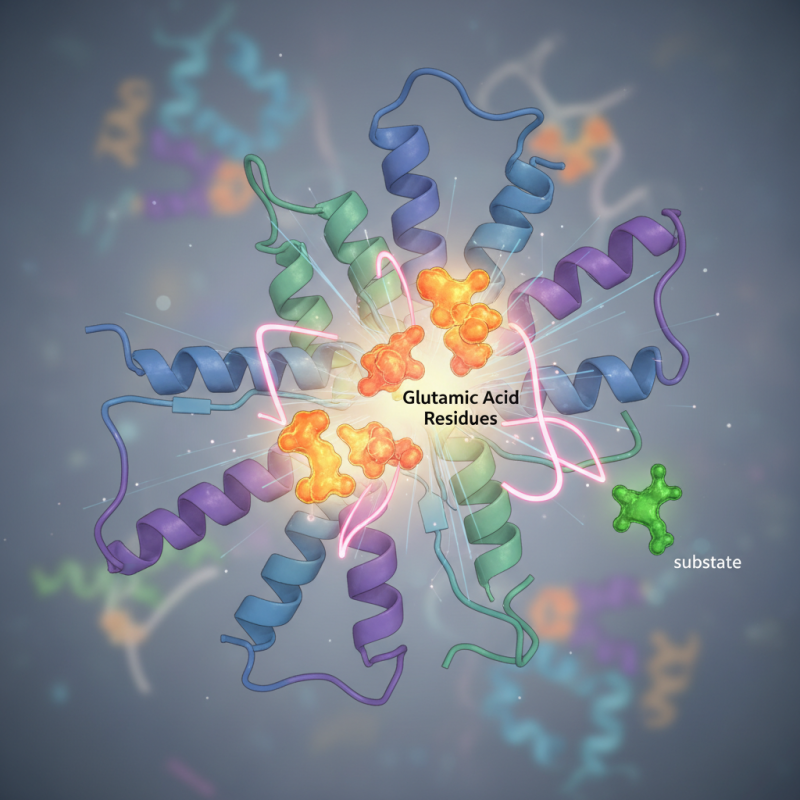
Understanding Glutamic Acid Residue: Basic Concepts in Biochemistry
Glutamic acid is an important amino acid in proteins. It plays a key role in many metabolic processes. This residue is often involved in enzyme function. Its acidic nature allows it to participate in various biochemical reactions. For instance, glutamic acid can stabilize protein structures. It forms hydrogen bonds with other residues. This interaction is crucial for protein folding and function.
Recent studies highlight the significance of glutamic acid in protein interactions. A report by the Biochemical Journal states that nearly 25% of proteins contain glutamic acid residues. This statistic underscores its prevalence in biological systems. Moreover, research shows that mutations in glutamic acid can lead to disease. For example, alterations in glutamic acid have been linked to neurodegenerative disorders. This emphasizes the need for understanding its role in protein dynamics.
But not all conclusions are simple. The interactions of glutamic acid are complex. There is still much to learn about its effects. Factors like pH and environmental conditions influence its behavior. Researchers are working to unravel these complexities. Understanding glutamic acid’s precise role could pave the way for new therapies. The journey into the world of protein biochemistry is filled with uncertainties, yet the significance of glutamic acid is undeniable.
The Role of Glutamic Acid in Protein Structure and Function
Glutamic acid plays a crucial role in protein structure and function. This amino acid contributes to the stability of proteins by forming hydrogen bonds and ionic interactions. As a negatively charged residue, glutamic acid can attract positively charged side chains, influencing the folding and stability of the protein.
In enzymes, glutamic acid often participates in catalysis. It can act as both a proton donor and acceptor. This dual role is vital in many biochemical reactions. For example, enzymes like pepsin use glutamic acid to activate their catalytic sites. It’s fascinating how such a simple molecule can dictate complex behaviors in proteins.
However, the effects of glutamic acid are not always straightforward. Misfolding and mutations can arise. These issues may lead to function loss or diseases. Understanding these delicate balance and interactions remains a challenge in biochemistry. The path to a clearer understanding requires continuous exploration and reflection on these fundamental principles of protein chemistry.
How to Understand Glutamic Acid Residue Effects in Proteins? - The Role of Glutamic Acid in Protein Structure and Function
| Protein Name | Glutamic Acid Residue Position | Function Impact | Structural Role |
|---|---|---|---|
| Myoglobin | E7 | Stabilizes heme binding | Involved in ligand positioning |
| Hemoglobin | E6 | Regulates O2 affinity | Critical for conformational change |
| Glutathione S-transferase | G55 | Facilitates detoxification | Affects substrate binding |
| Prothrombin | E10 | Influences clotting cascade | Essential for spatial arrangement |
| Caspase-3 | E164 | Regulates apoptosis | Contributes to active site formation |
Mechanisms of Interaction: Glutamic Acid and Protein Dynamics
Glutamic acid plays a significant role in protein dynamics. It often participates in various interactions that can greatly influence protein structure. By forming hydrogen bonds, glutamic acid residues can stabilize protein folding. This stability can determine how proteins function.
The interaction of glutamic acid with other amino acids is complex. For example, its negatively charged side chain can attract positively charged partners. This attraction can lead to essential conformational changes in the protein. Sometimes, these changes can enhance or inhibit enzyme activity. However, the exact mechanisms are not always well understood.
Understanding these interactions requires deeper research. Scientists still grapple with predicting how these residues affect overall protein behavior. There’s a need to explore the dynamic nature of these relationships. The unanswered questions can drive new discoveries in the field of biochemistry. Finding clarity may lead to advances in many areas, including drug design and therapeutic applications.
Understanding Glutamic Acid Residue Effects in Proteins
This bar chart represents the impact scores of glutamic acid residues on various proteins. The data shows how the presence of these residues influences protein dynamics, with scores reflecting their varying effects across different protein types.
Impact of Glutamic Acid Modifications on Enzymatic Activity
Glutamic acid is more than just a building block of proteins. Its modifications can significantly influence enzymatic activity. Researchers are uncovering just how these changes affect protein function. For example, phosphorylation of glutamic acid can alter enzyme structure and performance. These changes can enhance or inhibit catalytic activity.
Understanding these modifications can lead to exciting discoveries. Scientists are exploring how glutamic acid influences various biological processes, including metabolism and signaling. This exploration reveals that not all modifications yield positive outcomes. Some can lead to decreased efficiency or malfunctioning enzymes.
Tips: Pay attention to specific enzymes influenced by glutamic acid changes. Always consider the context of each modification. A small change can lead to unexpected results. Stay curious about how these interactions shape cellular functions. Being mindful of potential side effects is key to effective research.
Experimental Approaches to Study Glutamic Acid Effects in Proteins
Glutamic acid, a key amino acid in proteins, plays many roles in cellular processes. Understanding its effects is crucial. Experimental approaches can reveal how glutamic acid residues influence protein structure and function. Researchers commonly employ site-directed mutagenesis. This technique allows scientists to replace glutamic acid with other amino acids. Observing the resulting changes helps identify its specific contributions.
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy is also valuable. It provides insights into the protein's dynamics and interactions. NMR can show how the presence of glutamic acid influences binding sites. Additionally, molecular dynamics simulations can predict how these residues behave over time. These simulations depict real-time movements of the protein's atoms.
Tips: Keep an eye on temperature conditions during experiments. Variations can alter protein behavior. Remember, results may not always align perfectly with predictions. Discrepancies often lead to deeper understanding. Embrace surprises; they can spark innovative research questions.
